Reliability Papers
An Overview of Reliability
Abstract
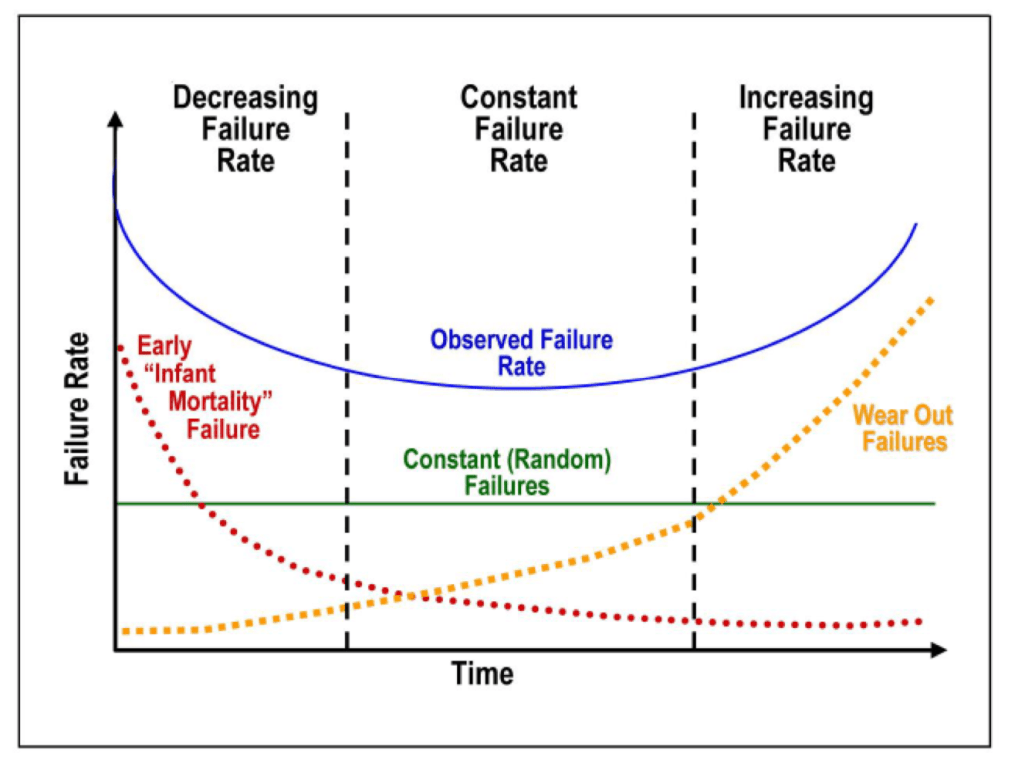
An overview of reliability engineering is presented here to serve as an introductory piece for some, or perhaps as a refresher. Much of the discussion here is general in coverage, and may suggest topics for further investigation.
The perspective here is at the electronic product or module level, which typically includes printed circuit board assemblies (PCBAs), power supply modules, software / firmware, product case, and user interface. The analytical and test tools discussed here are generally well suited for application to the electrical module or product hardware.
The intended audience here is the reliability engineer, or engineers wishing to go into that field. Another audience target may be the manager of that reliability engineering function, who wishes to learn more about the field of reliability engineering. The role of these persons is to promote the identification and completion of these reliability engineering tasks. They often act as the interface to other departments such as engineering, quality assurance, marketing, and manufacturing, so as to optimize the project activities related to reliability.
The goals of reliability engineering is to add value to the organization, reduce warranty costs, and satisfy customers, through the enhancement of product life. Activities include product analysis, product testing, failure analysis and reporting with recommendations.
Reliability Testing of Consumer Products
Abstract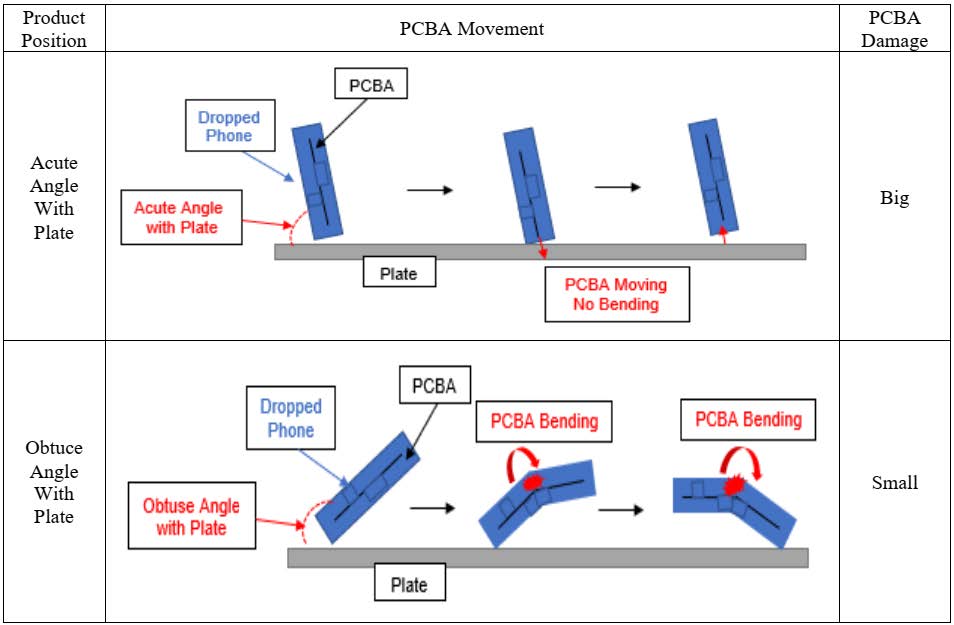
Reliability testing of consumer products is reviewed in several areas: how testing affects the expectation on the reliability, quality and safety of the consumer product, verification and validation of the product performance and specifications, setting the foundations for the manufacturing test and QA process, and planning for early returns and field failure rates.
Start up companies, such as crowd-funded companies are under pressure to launch the product (financing their production through pre-paid sales). We will look at reliability testing can be used to meet some of their objectives such as rapid time to market, reduced product cost and low product returns due to product failure.
Reliability Engineering Techniques for Consumer Products
Abstract
Consumer products have been thought of as being low priced and unreliable. We will look at some of the best approaches to use in designing and manufacturing consumer products in regard to reliability, and how these approaches can result in improved profitability without increasing cost, and some aspects of implementing these approaches. The approaches discussed here can be adapted to the special needs of the small startup companies.
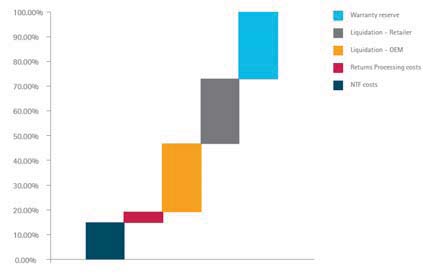
Many of the techniques involved with making consumer products more reliable are common to reliability tools used in any product and any quality level or cost level. For example if a toy arrives dead on arrival, this directly impact the profitability of the manufacturer. The manufacturer in consumer products often carries the burden of product returns whether those products are truly nonfunctional, or merely suffer from buyer’s remorse.
In the consideration for higher-end consumer products, such as smart phones or more higher-priced audio equipment, headsets, interconnect cables, computer accessories, again the consequences of reliability issues can result in nonfunctional products being returned as DOA.
We will look at first a review of the basics of reliability as it applies to consumer products, and some of the common misconceptions about this. And then we will look at some more realistic approaches to implementing the more reliable design, and aspects of manufacturing that affect product reliability. Examples will be given of simple steps that have been taken to improve the reliability of a product or the production process.
Start up companies, such as crowd-funded companies are under pressure to launch the product (financing their production through pre-paid sales). We will look at what reliability tools can be modified to meet some of their needs and help insure product reliability.
One of the benefits of implementing higher reliability into consumer products is the reduction in environmental waste. So for each improvement and product life there is a multiplier effect on the amount of waste generated in manufacturing, reduction in DOA’s, and the reduction in waste and disposal at the end of product life.
In each of these phases, we’ll look at how traditional reliability engineering techniques may be modified for consumer products or for a fast-paced startup company. Companies often don’t want to spend large sums on equipment, or and do not have the patience for the long-term life testing.
Introduction To HALT - Making Your Product Robust
Abstract
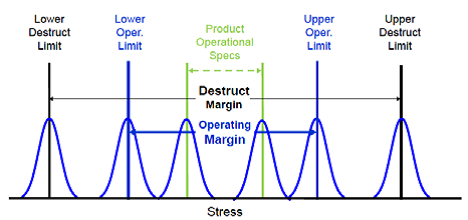
Reliability is highest when designed into products. One process to test for product reliability is the “Highly Accelerated Life Test” (HALT).
HALT is a test method to discover product design limits and failure modes through a series of increasing stress conditions, utilizing extreme thermal stresses and vibrations. Aimed largely at electronic Printed Circuit board products, it is highly effective in identifying stress operating limits and destruct limits, and in demonstrating failure modes in a matter of days that would normally show up in the field after weeks or months.
This article gives an explanation of what it will do, and what it will not do, and how to plan for it. The article discusses fixturing, equipment, facilities planning, setup, functional verification, and the actual running of the test. It also discusses the importance of failure analysis and corrective action, as well as HASS (Highly Accelerated Stress Screening), the manufacturing screening process based on HALT.

